Epidural in Labor: What It Is, Benefits, Risks, and What to Expect

Cradle of Nutrition
- 3 minutes read
Labor pain can be intense, and many women seek effective ways to manage it during childbirth. One of the most popular and effective pain relief methods is the epidural. In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about epidurals in labor—how they work, their benefits, potential risks, and when to consider getting one.
What Is an Epidural in Labor?
An epidural is a type of regional anesthesia commonly used to relieve pain during labor. It works by numbing the lower half of the body, helping mothers manage labor pain while staying awake and alert.
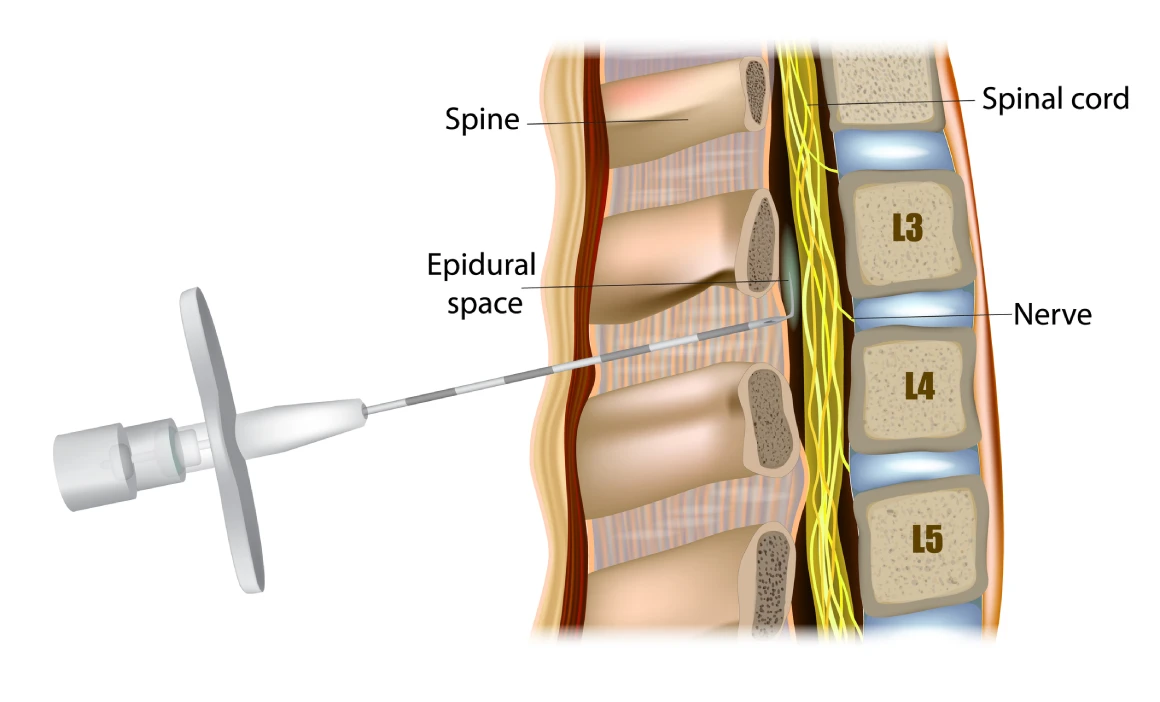
During the procedure, a combination of local anesthetics and pain-relieving medications is injected near the spinal cord in the lower back. Specifically, the medication is delivered into the epidural space — a small area located just outside the dura mater, which is the tough outer membrane surrounding the spinal cord. This space is usually found between the second and fifth lumbar vertebrae (L2 to L5).
By blocking pain signals from traveling to the brain, an epidural allows mothers to experience significant pain relief without losing movement or consciousness, making it one of the most effective and widely used methods of pain management during childbirth.
How Does an Epidural Work?
A trained anesthesiologist usually inserts a thin catheter into the epidural space. However, in some countries or healthcare settings, obstetricians may also perform this procedure. Through this catheter, medication is continuously or intermittently administered, providing effective and adjustable pain relief throughout labor.
Benefits of Epidural Pain Relief During Labor
- Highly effective pain management: Epidurals are considered the gold standard for labor pain relief, significantly reducing discomfort.
- Allows rest: By reducing pain, epidurals help mothers conserve energy during long labors.
- Adjustable sensation: Medication levels can be adjusted so mothers can still feel pressure and actively participate in pushing.
- Reduces stress: Less pain means less anxiety, helping labor progress more smoothly.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While epidurals are generally safe, there are some risks to be aware of:
- Drop in blood pressure: Monitored carefully to protect both mother and baby.
- Headache: Rare cases caused by spinal fluid leakage after the procedure.
- Limited mobility: Mothers typically must stay in bed once the epidural is administered.
- Labor changes: May slightly prolong the pushing stage or increase the chance of assisted delivery.
When Are Epidurals Given During Labor?
Epidural anesthesia is typically administered during the active stage of labor, once the cervix is dilated to around 4 to 5 centimeters and contractions have become regular.
Timing is important: giving an epidural too early (before active labor) may slow down labor progression, while giving it too late may not allow enough time for the medication to take full effect before delivery.
In most cases, doctors and midwives recommend placing the epidural once labor is well established, balancing effective pain relief with minimal risk to labor progress. However, the exact timing may vary based on the mother’s condition, labor progression, and hospital protocols.
Is an Epidural Safe?
Yes, epidurals are widely used and considered safe for most women and babies when given by qualified professionals. Continuous monitoring ensures that both mother and baby stay healthy during labor.
Who Should Avoid Epidurals?
Women with certain medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders, infections near the injection site, or spinal abnormalities, may not be suitable candidates for epidural anesthesia.
Final Thoughts
Epidurals provide effective pain relief during labor, allowing many women to have a more comfortable and less stressful childbirth experience. Discuss your pain management options with your healthcare provider to determine if an epidural is right for you.
By Erika Barabás
Related post:
Labor Stages 101: Pain Relief Options, Biological Processes, and What You Need to Know