Managing High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy: Types, Risks, and Safe Treatments

Cradle of Nutrition
- 3 minutes read
High blood pressure during pregnancy is a common but serious condition that can affect both mother and baby. Understanding the different types, the risks involved, and how to manage high blood pressure is essential for a safe and healthy pregnancy. This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know.
What Is High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy?
High blood pressure (also known as hypertension) occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls is too high. During pregnancy, this condition requires special attention because it can lead to complications for both the mother and the developing baby.
Types of High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy
1. Chronic Hypertension
- Diagnosed before pregnancy or before 20 weeks gestation
- May persist after delivery
- Requires careful monitoring and often medication
2. Gestational Hypertension
- Develops after 20 weeks of pregnancy
- No protein in the urine
- Can develop into preeclampsia if left untreated
3. Preeclampsia
- High blood pressure after 20 weeks with signs of organ damage or protein in urine
- Symptoms may include swelling, headaches, and visual disturbances
- Can lead to serious complications, including early delivery
4. Eclampsia
- A life-threatening complication that develops from preeclampsia
- Characterized by the onset of seizures in a pregnant woman with preeclampsia
- Represents a severe progression of preeclampsia, typically after the 20th week of pregnancy or shortly after delivery
- A medical emergency requiring immediate intervention to protect both mother and baby
How High Blood Pressure Affects Pregnancy
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can have serious consequences, including:
- Restricted blood flow to the placenta, which can cause:
- Low birth weight
- Premature birth
- Placental abruption
- Stillbirth
- Organ damage in the mother (kidneys, liver, brain)
- Increased risk of cesarean delivery
- Long-term cardiovascular risk for the mother
What Should Expectant Mothers Do?
Managing high blood pressure during pregnancy is possible with proper care. Here’s what you should do:
1. Get Early and Regular Prenatal Care
- Track blood pressure from the beginning
- Identify risks early
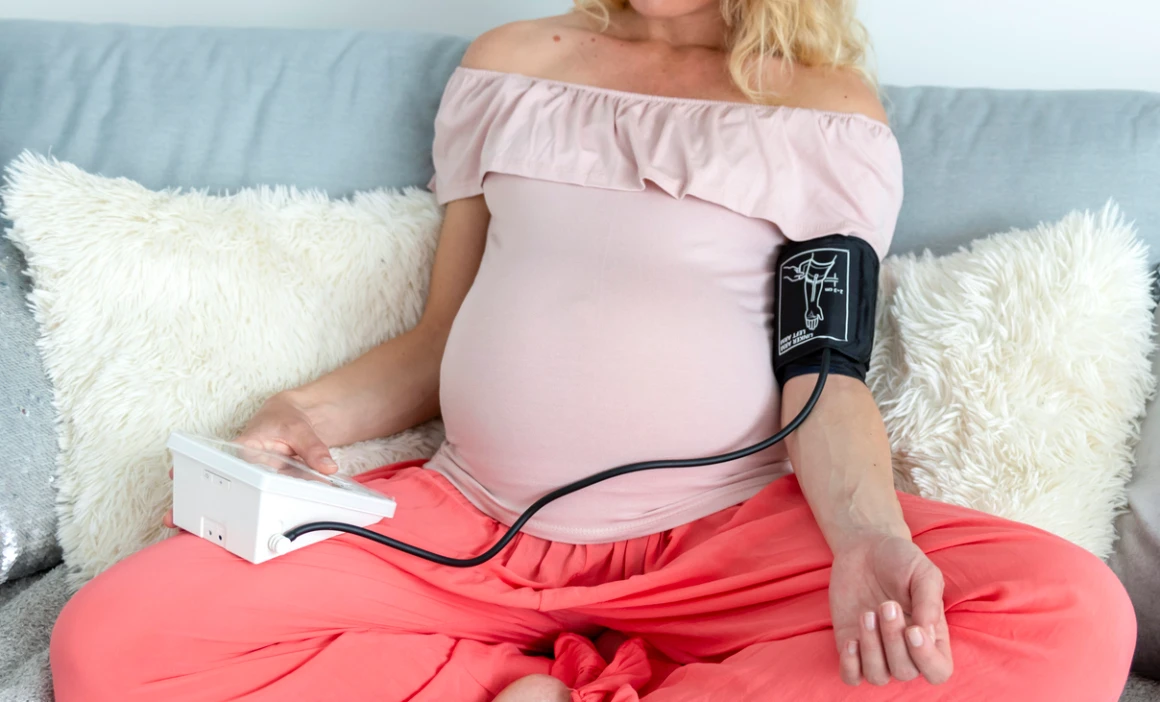
2. Monitor Your Blood Pressure
- Use a home blood pressure monitor
- Keep a log to show your healthcare provider
3. Follow a Healthy Lifestyle
- Eat a balanced, low-sodium diet
- Stay physically active (as recommended). Learn how to maintain a healthy exercise routine during pregnancy in Staying Active During Pregnancy
- Avoid smoking, alcohol, and excessive caffeine
4. Take Medication If Prescribed
- Safe medications: labetalol, nifedipine, methyldopa
- Do not stop or change medications without medical advice
5. Watch for Warning Signs
- Severe headaches
- Blurred vision or sensitivity to light
- Swelling in hands, face, or legs
- Upper abdominal pain
- Sudden weight gain
6. Prepare for Possible Early Delivery
- Severe hypertension or preeclampsia may require early induction or C-section
- Plan delivery in a hospital with a neonatal care unit if needed
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can high blood pressure be diagnosed before pregnancy?
Yes. If hypertension is present before pregnancy or before 20 weeks gestation, it’s classified as chronic hypertension.
2. Is high blood pressure during pregnancy dangerous?
Yes. If left unmanaged, it can lead to serious complications such as preeclampsia, organ damage, and preterm birth.
3. Can I have a healthy pregnancy with high blood pressure?
Absolutely. With proper monitoring, treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, most women can have a safe pregnancy.
4. Are blood pressure medications safe during pregnancy?
Yes. Some medications like labetalol, nifedipine, and methyldopa are considered safe. Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidance.
5. When should I seek emergency help?
If you experience severe headaches, vision changes, chest pain, or seizures, seek immediate medical attention.
Quick Overview
High blood pressure in pregnancy includes conditions like chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia. These can lead to serious complications such as low birth weight, preterm birth, and organ damage. Early prenatal care, lifestyle changes, blood pressure monitoring, and proper treatment are key to a safe pregnancy.
By Erika Barabás
References: